A natural gas generator operates by drawing fuel into an internal combustion engine and converting that motion into electrical power. The engine mixes natural gas with air inside the combustion chamber, and the spark plugs ignite the mix.
This action spins the alternator, which creates a steady flow of electricity for a home or business. When people ask how a natural gas generator works, the answer is a simple process of burning fuel and producing motion.
The system continues to run as long as the gas supply remains steady and the engine stays cool.
Natural gas burns cleanly and steadily because it is delivered through a fixed network of gas lines. This eliminates the need to store gasoline or diesel, allowing the engine to start smoothly and efficiently.
The clean burn reduces buildup inside the engine and supports long-term reliability. These traits make natural gas a strong choice for home backup power.
Key Takeaways
• A natural gas generator uses an internal combustion engine and alternator to produce electrical power during outages.
• The process depends on steady gas flow, clean burn, and timed ignition.
• Home units start on their own through a transfer switch and send power to key circuits.
• Natural gas offers clean burning and reliable fuel access compared with gasoline or diesel.
• Safe operation requires proper placement, clear airflow, and routine service.
How Natural Gas Generators Work (Step-by-Step)
A natural gas generator starts when the control board sends a signal to the engine. Gas moves through the regulator to maintain a steady pressure, and the engine mixes the fuel with air.
The spark plugs ignite the mix, turning the crankshaft and producing motion. These steps enable the alternator to generate electrical power during power outages.
The alternator sends electrical power to the home at a stable rate. These systems start fast and handle common power outages with ease. Some people ask how a gas generator works compared with natural gas units. Both use combustion, but natural gas comes through fixed lines, making long-term use easier.
Simple step sequence:
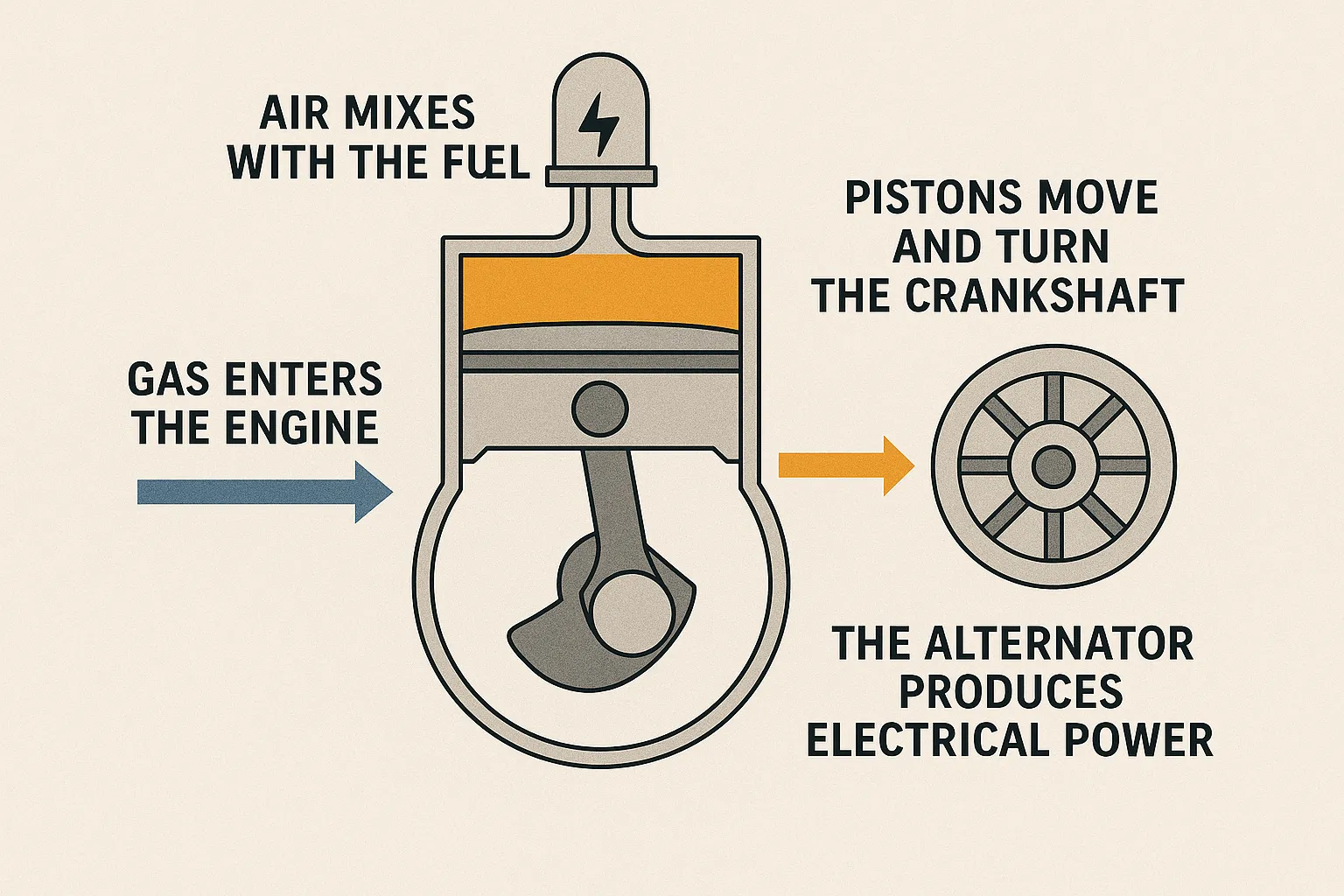
- Gas enters the engine.
- Air mixes with the fuel.
- Spark plugs ignite the mix.
- Pistons move and turn the crankshaft.
- The alternator produces electrical power.
Main Parts of a Natural Gas Generator
Main parts in simple terms:
- Engine: Creates motion.
- Alternator: Produces electrical power.
- Regulator: Controls gas pressure.
- Cooling System: Protects the engine from heat.
These parts work together to support power production during an outage.
The combustion chamber burns the fuel mix and moves the pistons. Spark plugs fire at the right moment during each ignition cycle. The alternator converts this motion into usable electricity for the home or business. Cooling and lubrication help keep the generator safe during prolonged use and prevent damage.
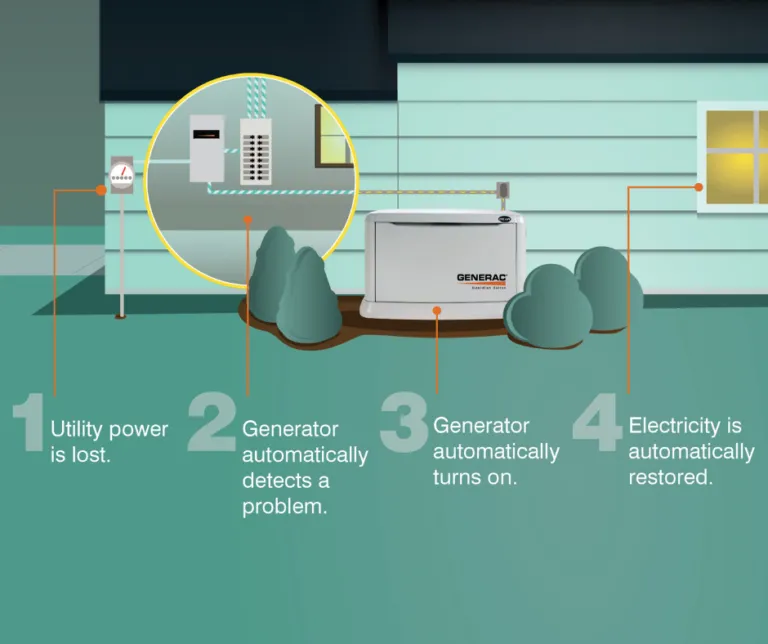
Home and Backup Generator Operation
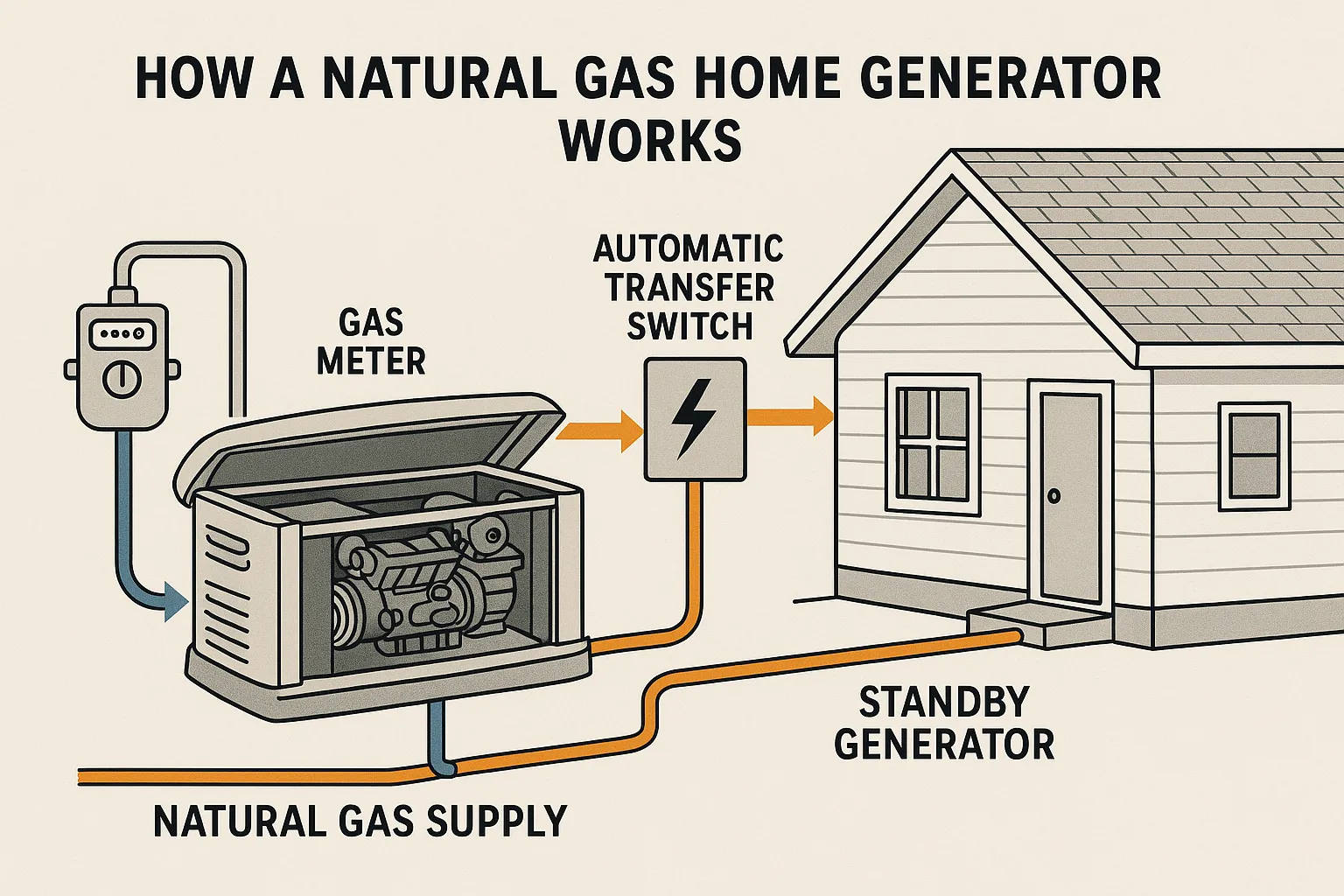
Many homeowners ask how a natural gas home generator works when planning for outages. The transfer switch monitors the electrical panel and activates the generator when power drops. It shifts selected circuits to generator power in seconds. This automatic process keeps key systems running until the grid returns.
A natural gas backup generator protects homes without the need for gasoline or diesel. This makes safe operation easier and maintains a consistent fuel supply.
The generator can support refrigerators, heating systems, medical devices, and communication tools. Grounded Electric installs these systems with care and detail, led by Barret Abramow.
When a storm cuts power, the transfer switch reacts and starts the generator. The engine starts and sends electricity to the selected circuits immediately. This fast response helps protect food, heating, and basic needs.
For help choosing a system, refer to our guide on selecting a generator for your home.

Portable and Brand-Specific Generator Types
Portable generators offer quick power for tools and short-term needs. They use the same internal combustion engine process but produce less output. Many models can run on natural gas with the right setup. They work well for small jobs or temporary needs.
Some may wonder how a natural gas-powered generator works or how a natural gas electric generator works. Both rely on controlled fuel burn and alternator motion. Natural gas facilitates long-term use because no liquid fuel is stored on-site.
Some ask how a natural gas portable generator works. It follows the same steps but supports fewer circuits. Grounded Electric installs many Generac systems and is certified to work with them.
This helps explain how a natural gas Generac generator works and why these units are trusted.
For fuel comparisons, review our guide on diesel generator vs propane generator.

Performance and Run Times
The efficiency of a natural gas generator depends on the load size and the engine’s condition. Clean fuel helps the engine maintain stability under various loads.
Many compare gasoline or diesel systems to see which fits their needs. Natural gas offers strong performance because it flows through stable underground lines.
Steady fuel pressure helps the engine burn the mix smoothly. The regulator controls pressure so the engine receives the right amount of gas. This helps prevent weak burns and maintains high efficiency. Strong pressure control also protects the engine during long-term use.
How long a natural gas generator can run? A natural gas generator can run for long periods because it uses a continuous gas supply. Most home standby units can operate 24 hours a day for several days as long as the engine stays within safe temperature limits and oil levels remain stable.
People also ask how long a natural gas generator can run continuously. Many units can run for extended periods if cooling and lubrication remain in good shape.
Costs and Value
The price of a natural gas generator depends on the unit size and installation needs. Larger properties may need higher power output. Portable generators cost less but support fewer devices. Grounded Electric reviews each site to help customers pick the right model.
Many also check the cost of the gas generator before buying a system. Costs include the unit, installation, and long-term service. For help planning, see our full gas generator cost guide.
Natural gas generators provide steady backup power, rapid start times, and cleaner operation compared to gasoline or diesel. The main limits include the need for a gas line and routine service.
Uses for Homes and Businesses
Natural gas generators protect homes, stores, and offices during outages. They maintain heat, refrigeration, and communication systems. Many businesses rely on them to avoid downtime. Grounded Electric helps each customer match the right generator size to their needs.
Some buildings use natural gas generators for longer run times. These setups require robust components and meticulous service planning. Grounded Electric checks each property to confirm safe and steady operation.
Safety and Maintenance
Safe operation begins with placing the generator outdoors or in a well-ventilated space. This prevents gas buildup and protects the home. Keep the area around the unit clear and free of clutter.
Routine maintenance includes oil changes, filter swaps, and spark plug checks. A technician like Bobby Mulholland can inspect the engine and wiring. These steps help the generator produce electricity safely. Grounded Electric offers service plans to support long-term performance.
Further Learning
For a full overview of generator types, setup steps, and safety tips, visit our generator guide. This resource helps homeowners choose, install, and maintain their systems with confidence.
If you need help selecting the right system or want expert guidance, you can schedule a consultation with Grounded Electric to receive clear recommendations tailored to your home’s specific needs.



